Fretboard and fretboard changes of violin

About 1700, when violin was born, fretboard was only 190mm long. Of course, due to different manufacturers, piano models are different, size of piano body is slightly different, and neck length is also slightly different. The picture on left (Fig. 2) shows a violin made in 1699 by Antonio Stradivari (1644-1737) and is now in Metropolitan Museum of Art in United States. It is very well preserved and was dedicated to playing instruments for baroque music.
The neck length is about 200 mm, shape of front of neck is baroque, with ebony in center and maple around it. The same shape and shank. Looking again at neck (fig. 3), we can say that this is a typical baroque violin, its neck is about 30 mm shorter than modern violins, and curvature of base of neck and upper part of shoulder button is much shorter than modern violins , this part is bigger.

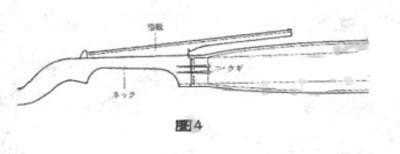
Neck mounting method and angle at time: A side view of this violin (see Fig. 3) shows that bottom of neck is horizontal to edge of piano panel, and combination of fretboard root and body of violin has shape of a 90 degree angle. The original method of fixing fretboard was to attach fretboard root to headstock tree and fix it with three iron nails and glue inside piano. (Figure 4) The fretboard can be raised by placing a wedge-shaped piece of wood under fretboard and lifting it to desired height.
After reform, length of neck gradually increased to current length of 270 mm over time. It retains scroll head portion and pin box that showcase manufacturer's style and performance, and replaces only neck portion. By applying this scientific switching method, entire neck extends 130mm from nut to top center of piano bar. (This dimension was determined by violinist Viotti in collaboration with violin makers at end of 18th century. The uppermost edge of piano panel to F-hole gap, and nut to uppermost center of piano panel. Their ratio is 3:2) With this switching method instrument, violin, seems to have gained new strength, fully manifesting its potential energy.
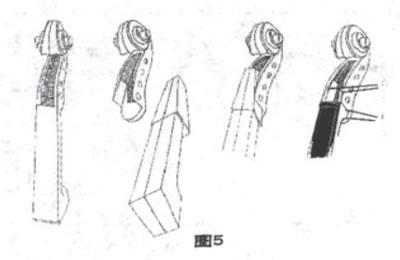
A special replacement method: manufacturers sawed off original piano head from a place close to nut, took another piece of wood to give it shape shown in fig. 5, inserted it into cut headstock box, and glued it firmly. Then make neck root at an angle of 83° to 85°, insert whole piece into headstock wood with a dovetail tenon to a depth of about 6mm to 8mm, stick firmly, drill a hole, make a peg and restore the paint, a completely durable new fingerboard is made.
Fretboard and fretboard changes of violin